Smart Solutions based on Internet of Things
Mate Liszi and Pavle Skocir
Description
Keywords: Smart meters, IoT platforms, IoT protocols, interoperability
H2020 challenge: Secure, clean and efficient energy
Knowledge and skills (P: prerequisite; D: desirable, but not necessary): Fundamentals of software design and architecture (P), Internet of Things (D), Communication technologies (LoRa, NB-IoT, LTE-M) (D), Hardware for analysing smart meters (D)
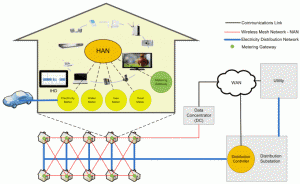
IoT (Internet of Things) technology can facilitate the operation of utility providers (electricity, gas, water) [1]. The public utility providers usually have units for consumption measurement (meters) at each consumer location without the possibility to read the consumption information remotely. This implies a vast number of meters that need to be physically frequented in regular intervals by the provider to acquire consumption information.
With IoT, a provider can acquire the measurement information remotely, without the need to physically access each meter or without the need for consumers to read the consumption values themselves and send the data to providers. These units are referred to as smart meters [2]. The deployment of smart meters increases the comfort of consumers since they do not have to take part in consumption reading and delivery process. Remote meter reading can be performed at a short distance, e.g., from a moving car on the street with a receiver, or at long distance by using stationary base stations [4]. Various technologies can be used for connecting smart meters with utility provider charging systems.
Questions that need answers
Students should analyse the current solutions in the area of smart metering. The following technological aspects should be evaluated:
- The hardware used for smart meters [5]
- Communication technologies, protocols used by smart meters [5]
- The overall system architecture (placement of gateways, databases, available applications and their functionalities) [3]
- IoT platforms for storage and analysis of smart metering data [6]
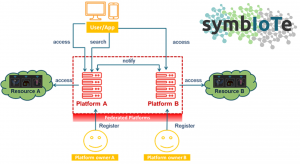
Smart metering data can be stored on different IoT platforms, e.g., on different platforms used by various national utility providers. Sometimes it is needed for certain applications (e.g., national regulators) to use information from different IoT platforms. The symbIoTe framework can facilitate access to data stored on different IoT platforms [7]. What needs to be done to integrate smart metering data from various platforms to the symbIoTe framework [8]?
- Student teams will need to analyse the current coverage of smart meters in the European countries and try to determine the areas which remain uncovered by smart meters.
- Smart meters can be used for more than just reporting on energy consumption [9]. Energy consumption information can be spread in one country over different smart metering platforms. Interoperability between these platforms is needed both within the national borders and between different countries. Why is interoperability between these different systems needed? Think not only about energy consumption measurements, but also other utilities (water, gas, etc.)
- symbIoTe project introduces the notion of platform federations [10]. Can this interoperability model be applied for some of the advanced usage scenarios of smart meters?
- Students need to analyse how the introduction of smart meters influences the labour market, i.e., how would it influence on the jobs of employees responsible for acquiring meter reading?
- What is the impact of applying a smart metering system at a public utility company in your country? What are your experiences about gathering consumption information (of the consumed gas, electricity, etc.?)? How can this solution influence the quality of life of the end consumers?
- What is the impact of determining accurate statistical reports about the consumed energy? Can this help in optimizing energy consumption?
- Does the data shared by smart metering solution need to be protected? What can be implied if the transfer of utility-related information is not secure?
Entrepreneurial Case Expert

Mate Liszi
TeamSoc21 Entrepreneurial Case Expert

Pavle Skocir
TeamSoc21 Entrepreneurial Case Expert
Case study students (Group 1)

Abdul-Razak Musah
TeamSoc21 Valencia 2019 Student

Esther Ródenas Moreno
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Katarina Mandaric
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Stiliyan Radev
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student
Case study students (Group 2)

Duca Marius Vlad
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Evelina Yordanova Marinova
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Maria del Mar Marejon de Giron
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student