Automotive Software Development and the Future of Electromobility
Hrvoje Vdovic and Dario Pevec
Description
Keywords: automotive software; electric vehicle; connected vehicle; autonomous vehicle; V2V; V2I
H2020 challenge: Smart, green and integrated transport
Knowledge and skills (P: prerequisite; D: desirable, but not necessary): Ability to work in a team (P), Knowledge about TCP/IP protocol stack (P), Basic programming skills (P), Presentation skills (P), Software design (D), Hardware design (D), Knowledge about automotive industry (D), and Entrepreneurial skills (D)
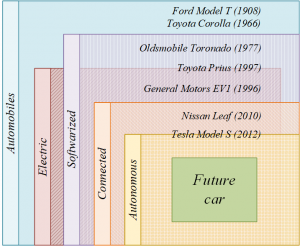
Not a single industry operating today exists, that is not at least partially governed by software, and automotive industry is no different. In 2008, a conservative assessment of the average software value per car was $425 and it is estimated to increase to $575 by 2020 [1], indicating a rise in value of over 35%. Furthermore, the worldwide market value of automotive embedded software is estimated to grow from $30 billion in 2008 to over $52 billion in 2020 [1].
Software is an indispensable part of today’s vehicles and its importance is perhaps the most significant in electric vehicles (EVs). EVs are actively pushing for a bigger share in the automotive market and are poised to replace internal combustion engine vehicles in the coming years as they emerged as a sustainable, green solution to reduce the CO2 emissions.
Software can increase an EV’s energy and cost efficiency, safety and comfort, all of which are significant aspects customers consider when purchasing a new vehicle. In addition to EVs, connected and autonomous vehicles are fast becoming a reality and with them the importance of software in vehicles increases tenfold.
The entrepreneurial case can be realized by identifying the possible automotive software improvements regarding above mentioned aspects important to EV customers (energy and cost efficiency, safety and comfort) and proposing a solution which addresses these challenges.
Questions that need answers
- Student teams will need to identify and provide more details about the current state of technology and software used in EVs [2], [3]. Students are expected to get familiar with the following:
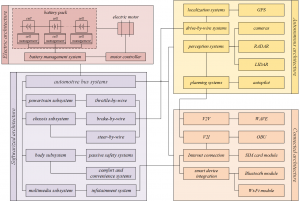
- In-vehicle networks, their capabilities and security (CAN, LIN, FlexRay, MOST, Ethernet) [4]
- Vehicle infotainment and operating systems (Windows Embedded Automotive, Android Auto, Apple CarPlay)
- Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) technology [5], [6]
- Vehicle perception (camera, radar and ultrasonic systems)
- Autopilot features of modern EVs [7]
Students will need to use the acquired knowledge of different technologies to address the chosen automotive software issue.
- Student teams will need to identify an aspect important to potential EV customer such as energy and cost efficiency, safety and comfort and offer a product or a service which solves a problem from that domain. Students will need to specify:
- Who are the product’s targeted customers?
- What is the added value of the product?
- What are the costs of development of the product?
- How will the product be distributed?
- What revenue streams are you expecting to finance your product development?
- Student teams will need to identify the impact of the solution on the the following stakeholders:
- Infrastructure owners
- Vehicle owners
- Vehicle users
Students will also need to explore the impact of the solution on the society as a whole, answering questions such as:
- Will the proposed solution reduce the number of accidents of the road?
- Will the proposed solution impact the labour market in any kind, causing people to lose jobs?
- Will the proposed solution reduce pollution?
- Will the proposed solution reduce traffic congestions?
Entrepreneurial Case Expert

Hrvoje Vdovic
TeamSoc21 Entrepreneurial Case Expert

Dario Pevec
TeamSoc21 Entrepreneurial Case Expert
Case study students (Group 1)

Daniel Olivares
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

David Gabora
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Norbert Serban
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Laszlo Preznyak
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student
Case study students (Group 2)

Adam Lany
TeamSoc21 Valencia2019 Student

Ivana Gace
TeamSoc21 Valencia 2019 Student